Maxwell Wisne; Yanpei Deng; Hilal Cansizoglu; Cameron Kopas; Josh Mutus; Venkat Chandrasekhar
Transport signatures of phase fluctuations in superconducting qubits Journal Article
In: Materials for Quantum Technology, vol. 4, pp. 046001, 2024.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags:
@article{Wisne2024,
title = {Transport signatures of phase fluctuations in superconducting qubits},
author = {Maxwell Wisne and Yanpei Deng and Hilal Cansizoglu and Cameron Kopas and Josh Mutus and Venkat Chandrasekhar},
url = {https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/2633-4356/ad9a47},
doi = {10.1088/2633-4356/ad9a47},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-12-13},
urldate = {2024-05-30},
journal = {Materials for Quantum Technology},
volume = {4},
pages = {046001},
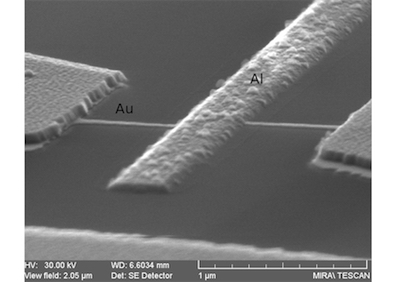
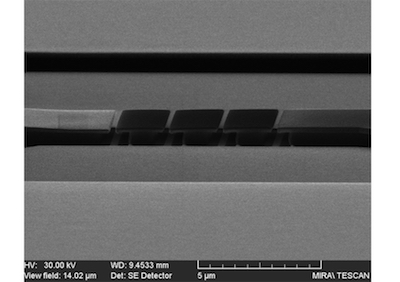
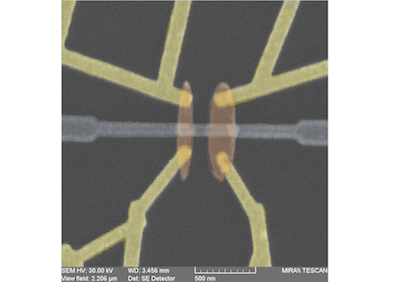
abstract = {Josephson junctions supply the nonlinear inductance element in superconducting qubits. In the widely used transmon configuration, where the junction is shunted by a large capacitor, the low charging energy minimizes the sensitivity of the qubit to charge noise while maintaining the necessary anharmonicity to qubit states. We report here low-frequency transport measurements on small standalone junctions and identically fabricated capacitively-shunted junctions that show two distinct features normally attributed to small capacitance junctions near zero bias: reduced switching currents and prominent finite resistance associated with phase diffusion in the current–voltage characteristic. Our transport data reveals the existence of phase fluctuations in transmons arising from intrinsic junction capacitance.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Maxwell Wisne; Yanpei Deng; Markus Lilja; Pertti Hakonen; Venkat Chandrasekhar
Mapping the topological proximity-induced gap of multiterminal Josephson junctions Journal Article
In: Physical Review Letters, vol. 133, pp. 246601, 2024.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags:
@article{Wisne2024b,
title = {Mapping the topological proximity-induced gap of multiterminal Josephson junctions},
author = {Maxwell Wisne and Yanpei Deng and Markus Lilja and Pertti Hakonen and Venkat Chandrasekhar},
url = {https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.133.246601},
doi = {10.1103/PhysRevLett.133.246601},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-12-09},
urldate = {2024-08-16},
journal = {Physical Review Letters},
volume = {133},
pages = {246601},
abstract = {Multiterminal Josephson junctions (MTJJs), devices in which a normal metal is in contact with three or more superconducting leads, have been proposed as artificial analogs of topological crystals. The topological nature of MTJJs manifests as a modulation of the quasiparticle density of states (DOS) in the normal metal that may be probed by tunneling measurements. We show that one can reveal this modulation by measuring the resistance of diffusive MTJJs with normal contacts, which shows rich structure as a function of the phase differences φi. Our approach demonstrates a simple yet powerful technique for exploring topological effects in MTJJs.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Kevin M. Ryan; Venkat Chandrasekhar
Enhanced Quasiparticle Relaxation in a Superconductor via the Proximity Effect Unpublished
2024.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags:
@unpublished{Ryan2024,
title = {Enhanced Quasiparticle Relaxation in a Superconductor via the Proximity Effect},
author = {Kevin M. Ryan and Venkat Chandrasekhar},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2409.05233v1},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-09-08},
urldate = {2024-09-08},
abstract = {Quasiparticle relaxation in pure superconductors is thought to be determined by the intrinsic inelastic scattering rate in the material. In certain applications, i.e. superconducting qubits and circuits, excess quasiparticles exist at densities far beyond the thermal equilibrium level, potentially leading to dephasing and energy loss. In order to engineer superconductors with shorter overall quasiparticle lifetimes, we consider the impact of a proximity layer on the transport of quasiparticles in a superconductor. We find that a normal metal layer can be used to significantly increase the relaxation rate of quasiparticles in a superconductor, as seen by a large reduction in the quasiparticle charge imbalance in a fully proximitized Cu/Al bilayer wire. The mechanism for this effect may be useful for preventing quasiparticle poisoning of qubits using carefully chosen proximity bilayers consisting of clean superconductors and disordered normal metals. },
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {unpublished}
}
Venkat Chandrasekhar
Current dependence of the low bias resistance of small capacitance Josephson junctions Journal Article
In: Physics Letters A, vol. 507, pp. 129493, 2024.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags:
@article{Chandrasekhar2024,
title = {Current dependence of the low bias resistance of small capacitance Josephson junctions},
author = {Venkat Chandrasekhar},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2024.129493},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-04-10},
journal = {Physics Letters A},
volume = {507},
pages = {129493},
abstract = {The dc current-voltage characteristics of small Josephson junctions reveal features that are not observed in larger
junctions, in particular, a switch to the finite voltage state at current values much less than the expected critical current
of the junction and a finite resistance in the nominally superconducting regime. Both phenomena are due to the increased
sensitivity to noise associated with the small capacitance of the Josephson junction and have been extensively studied
a few decades ago. Here I focus on the current bias dependence of differential resistance of the junction at low current
bias in the nominally superconducting regime, using a quantum Langevin equation approach that enables a physically
transparent incorporation of the noise environment of the junction. A similar approach might be useful in modeling the
sensitivity of superconducting qubits to noise in the microwave regime.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
junctions, in particular, a switch to the finite voltage state at current values much less than the expected critical current
of the junction and a finite resistance in the nominally superconducting regime. Both phenomena are due to the increased
sensitivity to noise associated with the small capacitance of the Josephson junction and have been extensively studied
a few decades ago. Here I focus on the current bias dependence of differential resistance of the junction at low current
bias in the nominally superconducting regime, using a quantum Langevin equation approach that enables a physically
transparent incorporation of the noise environment of the junction. A similar approach might be useful in modeling the
sensitivity of superconducting qubits to noise in the microwave regime.
Patrick W Krantz; Alexander Tyner; Pallab Goswami; Venkat Chandrasekhar
Intrinsic magnetism in KTaO3 heterostructures Journal Article
In: Applied Physics Letters, vol. 124, pp. 093102, 2024.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Magnetism, perovskite
@article{Krantz2024,
title = {Intrinsic magnetism in KTaO3 heterostructures},
author = {Patrick W Krantz and Alexander Tyner and Pallab Goswami and Venkat Chandrasekhar},
url = {https://pubs.aip.org/aip/apl/article/124/9/093102/3267521/Intrinsic-magnetism-in-KTaO3-heterostructures},
doi = {doi: 10.1063/5.0189956},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-02-27},
urldate = {2024-02-27},
journal = {Applied Physics Letters},
volume = {124},
pages = {093102},
abstract = {There has been intense recent interest in the two-dimensional electron gases (2DEGs) that form at the surfaces and interfaces of KTaO 3
(KTO), with the discovery of superconductivity at temperatures significantly higher than those of similar 2DEGs based on SrTiO 3 (STO).
Like STO heterostructures, these KTO 2DEGs are formed by depositing an overlayer on top of appropriately prepared KTO surfaces. Some
of these overlayers are magnetic, and the resulting 2DEGs show signatures of this magnetism, including hysteresis in the magnetoresistance
(MR). Here, we show that KTO 2DEGs fabricated by depositing AlOx on top of KTO also show hysteretic MR, indicative of long-range mag-
netic order, even though the samples nominally contain no intrinsic magnetic elements. The hysteresis appears in both the transverse and
longitudinal resistance in magnetic fields both perpendicular to and in the plane of the 2DEG. The hysteretic MR has different characteristic
fields and shapes for surfaces of different crystal orientations and vanishes above a few Kelvin. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations
indicate that the magnetism likely arises from Ta 4+ local moments created in the presence of oxygen vacancies.},
keywords = {Magnetism, perovskite},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
(KTO), with the discovery of superconductivity at temperatures significantly higher than those of similar 2DEGs based on SrTiO 3 (STO).
Like STO heterostructures, these KTO 2DEGs are formed by depositing an overlayer on top of appropriately prepared KTO surfaces. Some
of these overlayers are magnetic, and the resulting 2DEGs show signatures of this magnetism, including hysteresis in the magnetoresistance
(MR). Here, we show that KTO 2DEGs fabricated by depositing AlOx on top of KTO also show hysteretic MR, indicative of long-range mag-
netic order, even though the samples nominally contain no intrinsic magnetic elements. The hysteresis appears in both the transverse and
longitudinal resistance in magnetic fields both perpendicular to and in the plane of the 2DEG. The hysteretic MR has different characteristic
fields and shapes for surfaces of different crystal orientations and vanishes above a few Kelvin. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations
indicate that the magnetism likely arises from Ta 4+ local moments created in the presence of oxygen vacancies.
Patrick Krantz
Low Temperature Electrical Transport Behavior of AlOx / KTaO3 Based Two Dimensional Electron Gases PhD Thesis
2023.
@phdthesis{Krantz2023,
title = {Low Temperature Electrical Transport Behavior of AlOx / KTaO3 Based Two Dimensional Electron Gases},
author = {Patrick Krantz},
url = {http://www.nano.northwestern.edu/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/PWK_Dissertation.pdf},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-06-01},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {phdthesis}
}
Patrick W Krantz; Venkat Chandrasekhar
Nonlocal Differential Resistance in AlOx/KTaO3 Heterostructures Journal Article
In: 2022.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Magnetism, Mesoscopic quantum transport, perovskite, spin-orbit scattering
@article{Krantz2022,
title = {Nonlocal Differential Resistance in AlOx/KTaO3 Heterostructures},
author = {Patrick W Krantz and Venkat Chandrasekhar},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.12146},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-10-22},
abstract = {Local and nonlocal differential resistance measurements on Hall bars defined in AlOx/KTaO3 heterostructures show anomalous behavior that depends on the crystal orientation and the applied back gate voltage. The local differential resistance is asymmetric in the dc bias current, with an antisymmetric component that grows with decreasing gate voltage. More surprisingly, a large nonlocal differential resistance is observed that extends between measurement probes that are separated by 100s of microns. The potential source of this anomalous behavior is discussed.},
keywords = {Magnetism, Mesoscopic quantum transport, perovskite, spin-orbit scattering},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Patrick Krantz; Alex Tyner; Pallab Goswami; Venkat Chandrasekhar
Colossal Spontaneous Hall Effect and Emergent Magnetism in KTaO3 Two-Dimensional Electron Gases Journal Article
In: 2022.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: AMR, magnetic impurity, Magnetism, perovskite, Superconductivity
@article{nokey,
title = {Colossal Spontaneous Hall Effect and Emergent Magnetism in KTaO3 Two-Dimensional Electron Gases},
author = {Patrick Krantz and Alex Tyner and Pallab Goswami and Venkat Chandrasekhar},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.10534},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-09-21},
urldate = {2022-09-21},
abstract = {There has been intense recent interest in the two-dimensional electron gases (2DEGs) that form at the surfaces and interfaces of KTaO$_3$ (KTO), with the discovery of superconductivity at temperatures significantly higher than those of similar 2DEGs based on SrTiO$_3$ (STO). Here we demonstrate that KTO 2DEGs fabricated under conditions that suppress the superconductivity show a large spontaneous Hall effect at low temperatures. The transverse response is asymmetric in an applied perpendicular magnetic field and becomes hysteretic at millikelvin temperatures. The hysteresis is due to long range magnetic order arising from local Ta$^{4+}$ moments. However, the most striking features of the data are the asymmetry of the transverse response and the large spontaneous transverse resistance at zero field, which can be a significant fraction of the longitudinal resistance and depends on crystal orientation. Both effects are due to the presence of a dominant contribution to the transverse response that is symmetric in perpendicular field, suggesting that its origin is topological in nature. We argue that this contribution arises from Berry curvature dipoles coupled with nonequilibrium conditions induced by the measuring current.},
keywords = {AMR, magnetic impurity, Magnetism, perovskite, Superconductivity},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Venkat Chandrasekhar
Probing the topological band structure of diffusive multiterminal Josephson junction devices with conductance measurements Journal Article
In: Applied Physics Letters, vol. 121, pp. 222601, 2022.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Andreev reflection, Mesoscopic quantum transport, phase coherence, Proximity effect, Superconductivity
@article{nokey,
title = {Probing the topological band structure of diffusive multiterminal Josephson junction devices with conductance measurements},
author = {Venkat Chandrasekhar},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.04743
https://aip.scitation.org/doi/full/10.1063/5.0125708},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-09-10},
urldate = {2022-09-10},
journal = {Applied Physics Letters},
volume = {121},
pages = {222601},
abstract = {The energy of an Andreev bound state in a clean normal metal in contact with two superconductors disperses with the difference Δϕ in the superconducting phase between the superconductors in much the same way as the energies of electrons in a one-dimensional crystal disperse with the crystal momentum k of the electrons. A normal metal with n superconductors maps on to a n−1 dimensional crystal, each dimension corresponding to the phase difference ϕi between a specific pair of superconductors. The resulting band structure as a function of the phase differences {Δϕi} has been proposed to have a topological nature, with gapped regions characterized by different Chern numbers separated by regions where the gap in the quasiparticle spectrum closes. A similar complex evolution of the quasiparticle spectrum with {Δϕi} has also been predicted for diffusive normal metals in contact with multiple superconductors. Here we show that the variation of the density of states at the Fermi energy of such a system can be directly probed by relatively simple conductance measurements, allowing rapid characterization of the energy spectrum.},
keywords = {Andreev reflection, Mesoscopic quantum transport, phase coherence, Proximity effect, Superconductivity},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Kevin M. Ryan; Carlos G. Torres-Castanedo; Dominic P. Goronzy; David A. Garcia Wetter; Matthew J Reagor; Mark Field; Cameron J Kopas; Jayss Marshall; Michael J. Bedzyk; Mark C. Hersam; Venkat Chandrasekhar
Characterization of Nb films for superconducting qubits using phase boundary measurements Journal Article
In: Applied Physics Letters, vol. 121, pp. 202601, 2022.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: epitaxial, instrumentation, Superconductivity, superconductor
@article{Ryan2022,
title = {Characterization of Nb films for superconducting qubits using phase boundary measurements},
author = {Kevin M. Ryan and Carlos G. Torres-Castanedo and Dominic P. Goronzy and David A. Garcia Wetter and Matthew J Reagor and Mark Field and Cameron J Kopas and Jayss Marshall and Michael J. Bedzyk and Mark C. Hersam and Venkat Chandrasekhar},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.13125
https://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/5.0119932},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-07-26},
urldate = {2022-07-26},
journal = {Applied Physics Letters},
volume = {121},
pages = {202601},
abstract = {Continued advances in superconducting qubit performance require more detailed understandings of the many sources of decoherence. Within these devices, two-level systems arise due to defects, interfaces, and grain boundaries, and are thought to be a major source of qubit decoherence at millikelvin temperatures. In addition to Al, Nb is a commonly used metalization layer for superconducting qubits. Consequently, a significant effort is required to develop and qualify processes that mitigate defects in Nb films. As the fabrication of complete superconducting qubits and their characterization at millikelvin temperatures is a time and resource intensive process, it is desirable to have measurement tools that can rapidly characterize the properties of films and evaluate different treatments. Here we show that measurements of the variation of the superconducting critical temperature Tc with an applied external magnetic field H (of the phase boundary Tc−H) performed with very high resolution show features that are directly correlated with the structure of the Nb films. In combination with x-ray diffraction measurements, we show that one can even distinguish variations quality and crystal orientation of the grains in a Nb film by small but reproducible changes in the measured superconducting phase boundary.},
keywords = {epitaxial, instrumentation, Superconductivity, superconductor},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Taewan Noh; Andrew Kindseth; Venkat Chandrasekhar
The Nonlocal Superconducting Quantum Interference Device Journal Article
In: Physical Review B, vol. 104, pp. 064503, 2021.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Andreev reflection, Mesoscopic quantum transport, Proximity effect, Superconductivity
@article{Noh2020,
title = {The Nonlocal Superconducting Quantum Interference Device},
author = {Taewan Noh and Andrew Kindseth and Venkat Chandrasekhar},
url = {https://journals.aps.org/prb/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevB.104.064503},
doi = {10.1103/PhysRevB.104.064503},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-08-04},
urldate = {2020-11-12},
journal = {Physical Review B},
volume = {104},
pages = {064503},
abstract = {Superconducting quantum interference devices (SQUIDs) that incorporate two superconductor/insulator/superconductor (SIS) Josephson junctions in a closed loop form the core of some of the most sensitive detectors of magnetic and electric fields currently available. SQUIDs in these applications are typically operated with a finite voltage which generates microwave radiation through the ac Josephson effect. This radiation may impact the system being measured. We describe here a SQUID in which the Josephson junctions are formed from strips of normal metal (N) in good electrical contact with the superconductor (S). Such SNS SQUIDs can be operated under a finite voltage bias with performance comparable or potentially better than conventional SIS SQUIDs. However, they also permit a mode of operation that is based on the unusual interplay of quasiparticle currents and supercurrents in the normal metal of the Josephson junction. The method allows measurements of the flux dependence of the critical current of the SNS SQUID without applying a finite voltage bias across the SNS junction, enabling sensitive flux detection without generating microwave radiation.},
keywords = {Andreev reflection, Mesoscopic quantum transport, Proximity effect, Superconductivity},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Patrick Krantz; Venkat Chandrasekhar
Observation of zero-field transverse resistance in AlOx/SrTiO3 interface devices Journal Article
In: Physical Review Letters, vol. 127, pp. 036801, 2021.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: perovskite
@article{Krantz2020b,
title = {Observation of zero-field transverse resistance in AlOx/SrTiO3 interface devices},
author = {Patrick Krantz and Venkat Chandrasekhar},
url = {https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.127.036801},
doi = {10.1103/PhysRevLett.127.036801},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-07-16},
urldate = {2020-11-07},
journal = {Physical Review Letters},
volume = {127},
pages = {036801},
abstract = {Domain walls in AlOx/SrTiO3 (ALO/STO) interface devices at low temperatures give a rise to a new signature in the electrical transport of two-dimensional carrier gases formed at the surfaces or interfaces of STO-based heterostructures: a finite transverse resistance observed in Hall bars in zero external magnetic field. This transverse resistance depends on the local domain wall configuration and hence changes with temperature, gate voltage, thermal cycling and position along the sample, and can even change sign as a function of these parameters. The transverse resistance is observed below ≃ 70 K but grows and changes significantly below ≃40 K, the temperature at which the domain walls become increasingly polar. Surprisingly, the transverse resistance is much larger in (111) oriented heterostructures in comparison to (001) oriented heterostructures. Measurements of the capacitance between the conducting interface and an electrode applied to the substrate, which reflect the dielectric constant of the STO, indicate that this difference may be related to the greater variation of the temperature dependent dielectric constant with electric field when the electric field is applied in the [111] direction. The finite transverse resistance can be explained inhomogeneous current flow due to the preferential transport of current along domain walls that are not collinear with the nominal direction of the injected current.},
keywords = {perovskite},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Daniel G. Chica; Abishek K. Iyer; Matthew Cheng; Kevin M. Ryan; Patrick Krantz; Craig Laing; Roberto dos Reis; Venkat Chandrasekhar; Vinayak P. Dravid; Mercouri G. Kanatzidis
P2S5 Reactive Flux Method for the Rapid Synthesis of Mono- and Bimetallic 2D Thiophosphates M2–xM′xP2S6 Journal Article
In: Inorganic Chemistry, vol. 60, pp. 3502, 2021.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags:
@article{nokey,
title = {P2S5 Reactive Flux Method for the Rapid Synthesis of Mono- and Bimetallic 2D Thiophosphates M2–xM′xP2S6},
author = {Daniel G. Chica and Abishek K. Iyer and Matthew Cheng and Kevin M. Ryan and Patrick Krantz and Craig Laing and Roberto dos Reis and Venkat Chandrasekhar and Vinayak P. Dravid and Mercouri G. Kanatzidis},
url = {https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.0c03577},
doi = {10.1021/acs.inorgchem.0c03577},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-05-01},
urldate = {2021-05-01},
journal = {Inorganic Chemistry},
volume = {60},
pages = {3502},
abstract = {We report a reactive flux technique using the common reagent P2S5
and metal precursors developed to circumvent the synthetic bottleneck for producing
high-quality single- and mixed-metal two-dimensional (2D) thiophosphate materials.
For the monometallic compound, M2P2S6 (M = Ni, Fe, and Mn), phase-pure
materials were quickly synthesized and annealed at 650 °C for 1 h. Crystals of
dimensions of several millimeters were grown for some of the metal thiophosphates
using optimized heating profiles. The homogeneity of the bimetallic thiophosphates
MM′P2S6 (M, M′ = Ni, Fe, and Mn) was elucidated using energy-dispersive X-ray
spectroscopy and Rietveld refinement. The quality of the selected materials was
characterized by transmission electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy
measurements. We report two novel bimetallic thiophosphates, MnCoP2S6 and FeCoP2S6. The Ni2P2S6 and MnNiP2S6 flux reactions were monitored in situ using variable-temperature powder X-ray diffraction to understand the formation reaction pathways. The phases were directly formed in a single step at approximately 375 °C. The work functions of the semiconducting materials were determined and ranged from 5.28 to 5.72 eV.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
and metal precursors developed to circumvent the synthetic bottleneck for producing
high-quality single- and mixed-metal two-dimensional (2D) thiophosphate materials.
For the monometallic compound, M2P2S6 (M = Ni, Fe, and Mn), phase-pure
materials were quickly synthesized and annealed at 650 °C for 1 h. Crystals of
dimensions of several millimeters were grown for some of the metal thiophosphates
using optimized heating profiles. The homogeneity of the bimetallic thiophosphates
MM′P2S6 (M, M′ = Ni, Fe, and Mn) was elucidated using energy-dispersive X-ray
spectroscopy and Rietveld refinement. The quality of the selected materials was
characterized by transmission electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy
measurements. We report two novel bimetallic thiophosphates, MnCoP2S6 and FeCoP2S6. The Ni2P2S6 and MnNiP2S6 flux reactions were monitored in situ using variable-temperature powder X-ray diffraction to understand the formation reaction pathways. The phases were directly formed in a single step at approximately 375 °C. The work functions of the semiconducting materials were determined and ranged from 5.28 to 5.72 eV.
Venkat Chandrasekhar
In: Review of Scientific Instruments, vol. 91, pp. 023705, 2020.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: scanning probe, Tuning fork
@article{Chandrasekhar2020,
title = {A microchip microcontroller-based transducer controller for non-contact scanning probe microscopy with phase-locked loop, amplitude, and Q control},
author = {Venkat Chandrasekhar},
url = {https://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/1.5131657},
doi = {10.1063/1.5131657},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-02-11},
journal = {Review of Scientific Instruments},
volume = {91},
pages = {023705},
abstract = {An inexpensive yet versatile transducer controller for non-contact scanning probe microscopy (SPM) based on a PIC32 microcontroller from Microchip Technology, Inc is described. In addition to feedback control using the amplitude or phase of the signal from the non-contact transducer, the controller includes a phase-locked loop for frequency-shift feedback, as well as fixed-amplitude, quality factor (Q) control, and self-excitation modes. Apart from the input amplifiers, output buffers, and the Q-control circuit, all other functions of the controller are instantiated in software on the microchip, enabling rapid changes in operating parameters if needed. The controller communicates with a host personal computer via a simple serial connection. The controller has been tested with a quartz tuning-fork transducer but can be used with any oscillating non-contact transducer.},
keywords = {scanning probe, Tuning fork},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Patrick Krantz; Venkat Chandrasekhar
Etching sharp tips from thin metallic wires for tuning-fork-based scanning probe microscopy Journal Article
In: Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology B, vol. 38, pp. 024004, 2020.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: scanning probe, Tuning fork
@article{Krantz2020,
title = {Etching sharp tips from thin metallic wires for tuning-fork-based scanning probe microscopy},
author = {Patrick Krantz and Venkat Chandrasekhar},
url = {https://avs.scitation.org/doi/10.1116/1.5132848},
doi = {10.1116/1.5132848},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-02-07},
journal = {Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology B},
volume = {38},
pages = {024004},
abstract = {Sharp tips are critical for obtaining high resolution images in scanning probe microscopy (SPM), particularly in samples with large variations in topography. For tuning-fork-based SPM, such tips are commonly obtained by electrochemical etching of metallic wires (e.g., tungsten). Electrochemical etching of metallic wires is the preferred means of preparing tips for scanning tunneling microscopy (STM), and techniques for obtaining sharp tips have been investigated extensively. However, the requirements for STM and tuning-fork-based SPM are different. In particular, the wires used in STM are typically 250−500 μm in diameter, while the wires used for tuning-fork-based SPM are usually an order of magnitude narrower in order to minimize loading of the tuning fork: 25−50μm and sometimes down to a few micrometers in diameter. Consequently, many of the recipes developed for etching thicker metallic wires for STM tips do not give optimal results for smaller diameter wires. The authors describe here a modification of the etching circuit of Ibe et al. that significantly improves the reproducibility and reliability of the etching process for thin wires, and discuss the parameters that affect the aspect ratio of produced tips.
},
keywords = {scanning probe, Tuning fork},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Taewan Noh
Nonlocal correlations in a proximity-coupled normal metal PhD Thesis
Northwestern University, 2019.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Andreev reflection, Magnetism, Proximity effect, Superconductivity
@phdthesis{Noh2019,
title = {Nonlocal correlations in a proximity-coupled normal metal},
author = {Taewan Noh},
url = {http://www.nano.northwestern.edu/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/Thesis_Taewan_Noh.pdf},
year = {2019},
date = {2019-12-01},
urldate = {2019-12-01},
address = {2145 Sheridan Road, Evanston, IL 60208},
school = {Northwestern University},
abstract = {A superconductor-normal metal-superconductor (SNS) junction is capable of carrying supercurrent due to the Josephson coupling between the two superconductors. More inter- estingly, this coupling is maintained through the normal metal in a length determined by the Thouless energy of the normal metal, which can be a few microns, much longer than the case of conventional Josephson junction consisting of two superconductors separated by a thin insulator, where the thickness is only a few nanometers. This provides us with a capability of measuring the electric potential in the proximity-coupled normal metal by placing multiple probes on it. In particular, in this thesis we present the experimental results of our attempt to search nonlocal correlations mediated by a proximity-coupled normal metal via electrical transport measurements. At very low temperatures, with an overall dependence on the bias current seemingly analogous to that observed in prior experiments on NSN structures, the nonlocal differential resistance exhibits a peculiar dip in a small range of bias current. In addition to the qualitative explanation that accounts for the nonlocal differential resistance arising from the separation of quasiparticle current due to the Josephson coupling between the two superconductors, further analysis based on the quasiclassical theory of superconduc- tivity reveals that the central dip can be attributed to penetration of pair correlations into the proximity-coupled normal metal from both superconductors in a coherent manner. While the processes analogous to crossed Andreev reflection and elastic cotunneling observed in a superconductor are yet to be found, our data and analysis provide insights on the physics behind the interplay between the quasiparticle current and the supercurrent which gives rise to the observed nonlocal correlations in a proximity-coupled normal metal.
Beside the nonlocal correlations in a proximity-coupled normal metal, we also investigated electrical transport through a heterostructure including double superconductor-ferromagnet (FS) interfaces. In addition to a typical signature of spin imbalance due to the Zeeman splitting in the density of states (DOS) of the quasiparticles in a superconductor, an inter- esting feature in a small range of bias current has been observed, which might be related to spin-dependent phenomena at FS interfaces although further investigation in a simpler geometry of the sample is required to elucidate the exact mechanism.},
keywords = {Andreev reflection, Magnetism, Proximity effect, Superconductivity},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {phdthesis}
}
Beside the nonlocal correlations in a proximity-coupled normal metal, we also investigated electrical transport through a heterostructure including double superconductor-ferromagnet (FS) interfaces. In addition to a typical signature of spin imbalance due to the Zeeman splitting in the density of states (DOS) of the quasiparticles in a superconductor, an inter- esting feature in a small range of bias current has been observed, which might be related to spin-dependent phenomena at FS interfaces although further investigation in a simpler geometry of the sample is required to elucidate the exact mechanism.
V. V. Bal; Z. Huang; K. Han; Ariando; T. Venkatesan; V. Chandrasekhar
Low temperature magnetoresistance of (111) (La0.3Sr0.7)(Al0.65Ta0.35)/SrTiO3 Journal Article
In: Physical Review B, vol. 99, pp. 035408, 2019.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: epitaxial, magnetic impurity, Magnetism, perovskite, phase coherence, spin glass, Superconductivity
@article{Bal2018,
title = {Low temperature magnetoresistance of (111) (La0.3Sr0.7)(Al0.65Ta0.35)/SrTiO3},
author = {V. V. Bal and Z. Huang and K. Han and Ariando and T. Venkatesan and V. Chandrasekhar},
url = {https://journals.aps.org/prb/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevB.99.035408},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.99.035408},
year = {2019},
date = {2019-01-03},
journal = {Physical Review B},
volume = {99},
pages = {035408},
abstract = {The two-dimensional conducting interfaces in SrTiO3-based systems are known to show a variety of coexisting and competing phenomena in a complex phase space. Magnetoresistance measurements, which are typically used to extract information about the various interactions in these systems, must be interpreted with care, since multiple interactions can contribute to the resistivity in a given range of magnetic field and temperature. Here we review all the phenomena that can contribute to transport in SrTiO3-based conducting interfaces at low temperatures. We apply this understanding to the perpendicular magnetoresistance data of the high-mobility system of (111) oriented (La0.3Sr0.7)(Al0.65Ta0.35)O3/STO heterostructures, and find an excess negative magnetoresistance contribution which cannot be explained by weak localization alone. We argue that contributions from magnetic scattering as well as electron-electron interactions, combined with weak localization/antilocalization, can provide a possible explanation for the observed magnetoresistance.},
keywords = {epitaxial, magnetic impurity, Magnetism, perovskite, phase coherence, spin glass, Superconductivity},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Varada Vilas Bal
Transport Measurements on (111) Oriented (La0.3Sr0.7)(Al0.65Ta0.35)O3/SrTiO3 Heterostructures PhD Thesis
Northwestern University, 2018.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: epitaxial, Kondo effect, magnetic impurity, Magnetism, perovskite, spin-orbit scattering, Superconductivity, superconductor
@phdthesis{Bal2018b,
title = {Transport Measurements on (111) Oriented (La0.3Sr0.7)(Al0.65Ta0.35)O3/SrTiO3 Heterostructures},
author = {Varada Vilas Bal},
url = {http://www.nano.northwestern.edu/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/BalVarada_PhD_Thesis.pdf},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-09-01},
address = {Department of Physics},
school = {Northwestern University},
abstract = {At the interface of two dissimilar entities, something novel can emerge. This idea has driven a vast amount of fruitful work on semiconductor interfaces, and given us the digi- tal revolution. In the past decade, remarkable progress has been made in the synthesis and understanding of interfaces between oxides, opening up new avenues to explore fundamen- tal emergent physics at the interface, as well as to provide viable candidates to augment or even surpass the performance of conventional semiconductor electronics. The two- dimensional conducting interface in the (001) LaAlO3/SrTiO3 system is the most studied example of oxide interfaces, showing a wide range of coexisting and competing phenomena such as superconductivity, superconductor-insulator transitions, magnetism, and spin- orbit interactions. The (111) oriented LaAlO3/SrTiO3 system has been recently found to have a few surprises of its own, with intriguing anisotropies in many transport properties along different in-plane crystal directions. This thesis presents the first results on a different SrTiO3 based system: the conducting interface between (La0.3Sr0.7)(Al0.65Ta0.35) and (111) oriented SrTiO3, which has a smaller strain as compared to the LaAlO3/SrTiO3 system. Electrical transport measurements at cryogenic temperatures reveal that no systematic anisotropy is seen in transport properties, unlike in the case of (111) oriented LaAlO3/SrTiO3. High-field magnetotransport shows the presence of high-mobility carri- ers at high electron densities, and exhibits multiband behavior, tunable in situ using an electrical back-gate, similar to the LaAlO3/SrTiO3 system. The data allow us to draw specific conclusions about band ordering in the system, and point to possible differences between the band ordering in (111) (La0.3Sr0.7)(Al0.65Ta0.35)O3/SrTiO3 and (001) as well as (111) oriented LaAlO3/SrTiO3. Low-field magnetotransport reveals that a strong spin- orbit interaction emerges in the regime of low electron density, when the high-mobility carriers are depleted from the system, a trend which is opposite to that observed in (001) oriented LaAlO3/SrTiO3. The most striking feature is that at millikelvin temperatures, in the regime of low electron densities, concomitant with the development of strong spin- orbit interaction, magnetic order emerges.},
keywords = {epitaxial, Kondo effect, magnetic impurity, Magnetism, perovskite, spin-orbit scattering, Superconductivity, superconductor},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {phdthesis}
}
V. V. Bal; Z. Huang; K. Han; Ariando; T. Venkatesan; V. Chandrasekhar
Strong spin-orbit coupling and magnetism in (111) (La0.3Sr0.7)(Al0.65Ta0.35)/SrTiO3 Journal Article
In: Physical Review B, vol. 98, pp. 085416, 2018.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: epitaxial, Magnetism, perovskite
@article{Bal2017b,
title = {Strong spin-orbit coupling and magnetism in (111) (La0.3Sr0.7)(Al0.65Ta0.35)/SrTiO3},
author = {V. V. Bal and Z. Huang and K. Han and Ariando and T. Venkatesan and V. Chandrasekhar},
url = {https://journals.aps.org/prb/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevB.98.085416},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.98.085416},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-08-07},
journal = {Physical Review B},
volume = {98},
pages = {085416},
abstract = {Two-dimensional conducting interfaces in SrTiO3-based heterostructures display a variety of coexisting and competing physical phenomena, which can be tuned by the application of a gate voltage. (111) oriented heterostructures have recently gained attention due to the possibility of finding exotic physics in these systems due to their hexagonal surface crystal symmetry. In this work, we use magnetoresistance to study the evolution of spin-orbit interaction and magnetism in (111) oriented (La0.3Sr0.7)(Al0.65Ta0.35)O3/SrTiO3. At more positive values of the gate voltage, which correspond to high carrier densities, we find that transport is multiband, and dominated by high-mobility carriers with a tendency toward weak localization. At more negative gate voltages, the carrier density is reduced, the high-mobility bands are depopulated, and weak antilocalization effects begin to dominate, indicating that spin-orbit interaction becomes stronger. At millikelvin temperatures, at gate voltages corresponding to the strong spin-orbit regime, we observe hysteresis in magnetoresistance, indicative of ferromagnetism in the system. Our results suggest that in the (111) (La0.3Sr0.7)(Al0.65Ta0.35)O3/SrTiO3 system, low-mobility carriers that experience strong spin-orbit interactions participate in creating magnetic order in the system.},
keywords = {epitaxial, Magnetism, perovskite},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Samuel Kenneth Davis; Zhen Huang; Kun Han; Ariando; Thirumalai Venkatesan; Venkat Chandrasekhar
Anisotropic superconductivity and frozen electronic states at the (111) LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface Journal Article
In: Physical Review B, vol. 98, pp. 024504, 2018.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: perovskite, Superconductivity
@article{davis_111_superconductivity_2017,
title = {Anisotropic superconductivity and frozen electronic states at the (111) LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface},
author = {Samuel Kenneth Davis and Zhen Huang and Kun Han and Ariando and Thirumalai Venkatesan and Venkat Chandrasekhar},
url = {https://journals.aps.org/prb/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevB.98.024504},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.98.024504},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-07-09},
journal = {Physical Review B},
volume = {98},
pages = {024504},
abstract = {We report measurements of the superconducting properties of the two-dimensional (2D) gas that forms at the interface between LaAlO3 (LAO) and SrTiO3 (STO) in the (111) crystal orientation, a system that permits in situ tuning of carrier density and disorder by means of a back-gate voltage Vg. Like the (001) oriented LAO/STO interface, superconductivity at the (111) LAO/STO interface can be tuned by Vg. The 2D superconductivity in these (111) LAO/STO samples shows an in-plane anisotropy, being different along different interface crystal directions, and “remembers” the disorder landscape at which they are cooled through the superconducting transition. The low energy scale and other characteristics of this memory effect distinguish it from charge-trapping effects previously observed in (001) interface samples.},
keywords = {perovskite, Superconductivity},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
S. Davis; Z. Huang; K. Han; Ariando; T. Venkatesan; V. Chandrasekhar
Signatures of Electronic Nematicity in (111) LaAlO3/SrTiO3 Interfaces Journal Article
In: Physical Review B, vol. 97, pp. 041408(R), 2018.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: epitaxial, perovskite
@article{Davis2017b,
title = {Signatures of Electronic Nematicity in (111) LaAlO3/SrTiO3 Interfaces},
author = {S. Davis and Z. Huang and K. Han and Ariando and T. Venkatesan and V. Chandrasekhar},
url = {https://journals.aps.org/prb/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevB.97.041408},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.97.041408},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-01-16},
journal = {Physical Review B},
volume = {97},
pages = {041408(R)},
abstract = {Symmetry breaking is a fundamental concept in condensed matter physics whose presence often heralds new phases of matter. For instance, the breaking of time reversal symmetry is traditionally linked to magnetic phases in a material, while the breaking of gauge symmetry can lead to superfluidity/superconductivity. Nematic phases are phases in which rotational symmetry is broken while maintaining translational symme- try, and are traditionally associated with liquid crystals. Electronic nematic states where the or- thogonal in-plane crystal directions have different electronic properties have garnered a great deal of attention after their discovery in Sr3Ru2O7, multiple iron based superconductors, and in the superconducting state of CuBiSe. Here we demonstrate the existence of an electronic ne- matic phase in the two-dimensional carrier gas that forms at the (111) LaAlO3 (LAO)/SrTiO3 (STO) interface that onsets at low temperatures, and is tunable by an electric field. },
keywords = {epitaxial, perovskite},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Samuel Kenneth Davis
Emergent Phenomena at the (111) LaAlO3/SrTiO3 Interface PhD Thesis
Department of Physics, Northwestern University, 2017.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Magnetism, perovskite, Superconductivity
@phdthesis{Davis2017c,
title = {Emergent Phenomena at the (111) LaAlO3/SrTiO3 Interface},
author = {Samuel Kenneth Davis},
url = {http://www.nano.northwestern.edu/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/Davis-Thesis.pdf},
year = {2017},
date = {2017-12-01},
school = {Department of Physics, Northwestern University},
abstract = {In his Nobel lecture Herbert Kroemer famously stated that “The interface is the device”. While he made this statement in the context of semiconducting heterostructures, it has proven to be just as relevant for more complex materials, such as the transition metal oxides. In particular, the 2-D conducting gas that forms at the interface between two transition metal oxides LaAlO3 and SrTiO3 (LAO/STO) has shown that a system containing a rich phase space of phenomena can arise from the interface of two relatively boring insulators. These phenomena include superconductivity, magnetism, gate tuned metal to insulator and superconductor to insulator transitions as well as evidence of large spin-orbit coupling at the interface. While the observation of these effects has produced more than a decade of fervent research on the LAO/STO interface, these previous efforts have focused mainly on the (001) crystal orientation of the LAO/STO interface. This thesis presents the results of some of the first studies on the (111) orientation of the LAO/STO interface, which not only has a more complex interfacial symmetry, but also shows new emergent phenomena. The most striking of which is the observation of strong, in-plane, anisotropy in the almost all of interface’s electrical transport properties. The thesis will identify not only identify where this anisotropy “lives” in the (111) LAO/STO interface, but also examine the energy scale at which it onsets. These results are evidence of an electronic nematic state that breaks the rotational symmetry of the sample. Finally, it will explore how this anisotropy impacts the other phenomena present at the interface, superconductivity and ferromagnetism.},
keywords = {Magnetism, perovskite, Superconductivity},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {phdthesis}
}
S. Davis; Z. Huang; K. Han; Ariando; T. Venkatesan; V. Chandrasekhar
Magnetoresistance in the superconducting state at the (111) LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface Journal Article
In: Physical Review B, vol. 96, pp. 134502, 2017.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: epitaxial, Magnetism, perovskite, Superconductivity
@article{Davis2017,
title = {Magnetoresistance in the superconducting state at the (111) LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface},
author = {S. Davis and Z. Huang and K. Han and Ariando and T. Venkatesan and V. Chandrasekhar},
url = {https://journals.aps.org/prb/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevB.96.134502},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.96.134502},
year = {2017},
date = {2017-07-11},
journal = {Physical Review B},
volume = {96},
pages = {134502},
abstract = {Condensed-matter systems that simultaneously exhibit superconductivity and ferromagnetism are rare due the antagonistic relationship between conventional spin-singlet superconductivity and ferromagnetic order. In materials in which superconductivity and magnetic order are known to coexist (such as some heavy-fermion materials), the superconductivity is thought to be of an unconventional nature. Recently, the conducting gas that lives at the interface between the perovskite band insulators LaAlO3 (LAO) and SrTiO3 (STO) has also been shown to host both superconductivity and magnetism. Most previous research has focused on LAO/STO samples in which the interface is on the (001) crystal plane. Relatively little work has focused on the (111) crystal orientation, which has hexagonal symmetry at the interface, and has been predicted to have potentially interesting topological properties, including unconventional superconducting pairing states. Here we report measurements of the magnetoresistance of (111) LAO/STO heterostructures at temperatures at which they are also superconducting. As with the (001) structures, the magnetoresistance is hysteretic, indicating the coexistence of magnetism and superconductivity, but in addition, we find that this magnetoresistance is anisotropic. Such an anisotropic response is completely unexpected in the superconducting state and suggests that (111) LAO/STO heterostructures may support unconventional superconductivity.},
keywords = {epitaxial, Magnetism, perovskite, Superconductivity},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
V.V Bal; Zhen Huang; Kun Han; Ariando; T Venkatesan; Venkat Chandrasekhar
Electrostatic tuning of magnetism at the conducting (111) (La0.3Sr0.7)(Al0.65Ta0.35)/SrTiO3 interface Journal Article
In: Applied Physics Letters, vol. 111, no. 8, pp. 081604, 2017.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: epitaxial, Magnetism, perovskite
@article{Bal2017,
title = {Electrostatic tuning of magnetism at the conducting (111) (La0.3Sr0.7)(Al0.65Ta0.35)/SrTiO3 interface},
author = {V.V Bal and Zhen Huang and Kun Han and Ariando and T Venkatesan and Venkat Chandrasekhar},
url = {http://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/1.4986912},
doi = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.4986912},
year = {2017},
date = {2017-06-06},
journal = {Applied Physics Letters},
volume = {111},
number = {8},
pages = {081604},
abstract = {We present measurements of the low temperature electrical transport properties of the two dimensional carrier gas that forms at the interface of (111) (La0.3Sr0.7)(Al0.65Ta0.35)/SrTiO3 (LSAT/STO) as a function of applied back gate voltage, Vg. As is found in (111) LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interfaces, the low-field Hall coefficient is electron-like, but shows a sharp reduction in magnitude below Vg∼ 20 V, indicating the presence of hole-like carriers in the system. This same value of Vg correlates approximately with the gate voltage below which the magnetoresistance evolves from nonhysteretic to hysteretic behavior at millikelvin temperatures, signaling the onset of magnetic order in the system. We believe our results can provide insight into the mechanism of magnetism in SrTiO3 based systems.},
keywords = {epitaxial, Magnetism, perovskite},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
S Davis; V Chandrasekhar; Z Huang; K Han; Ariando; T Venkatesan
Anisotropic multicarrier transport at the (111) LaAlO_3/SrTiO_3 interface Journal Article
In: Phys. Rev. B, vol. 95, no. 3, pp. 035127, 2017.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: epitaxial, perovskite
@article{davis_anisotropic_2017,
title = {Anisotropic multicarrier transport at the (111) LaAlO_3/SrTiO_3 interface},
author = {S Davis and V Chandrasekhar and Z Huang and K Han and Ariando and T Venkatesan},
url = {http://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevB.95.035127},
doi = {10.1103/PhysRevB.95.035127},
year = {2017},
date = {2017-01-01},
urldate = {2017-01-17},
journal = {Phys. Rev. B},
volume = {95},
number = {3},
pages = {035127},
abstract = {The conducting gas that forms at the interface between LaAlO3 and SrTiO3 has proven to be a fertile playground for a wide variety of physical phenomena. The bulk of previous research has focused on the (001) and (110) crystal orientations. Here we report detailed measurements of the low-temperature electrical properties of (111) LAO/STO interface samples. We find that the low-temperature electrical transport properties are highly anisotropic in that they differ significantly along two mutually orthogonal crystal orientations at the interface. While anisotropy in the resistivity has been reported in some (001) samples and in (110) samples, the anisotropy in the (111) samples reported here is much stronger and also manifests itself in the Hall coefficient as well as the capacitance. In addition, the anisotropy is not present at room temperature and at liquid nitrogen temperatures, but only at liquid helium temperatures and below. The anisotropy is accentuated by exposure to ultraviolet light, which disproportionately affects transport along one surface crystal direction. Furthermore, analysis of the low-temperature Hall coefficient and the capacitance as a function of back gate voltage indicates that in addition to electrons, holes contribute to the electrical transport.},
keywords = {epitaxial, perovskite},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Samuel Kenneth Davis; Zhen Huang; Kun Han; Ariando; Thirumalai Venkatesan; Venkat Chandrasekhar
Electrical Transport Anisotropy Controlled by Oxygen Vacancy Concentration in (111) LaAlO_3 /SrTiO_3 Interface Structures Journal Article
In: Advanced Materials Interfaces, pp. 1600830, 2016, ISSN: 21967350.
Links | BibTeX | Tags: epitaxial, perovskite
@article{davis_electrical_2016,
title = {Electrical Transport Anisotropy Controlled by Oxygen Vacancy Concentration in (111) LaAlO_3 /SrTiO_3 Interface Structures},
author = { Samuel Kenneth Davis and Zhen Huang and Kun Han and Ariando and Thirumalai Venkatesan and Venkat Chandrasekhar},
url = {http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/admi.201600830},
doi = {10.1002/admi.201600830},
issn = {21967350},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-12-01},
urldate = {2016-12-09},
journal = {Advanced Materials Interfaces},
pages = {1600830},
keywords = {epitaxial, perovskite},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Manan Mehta
Interplay between superconductivity and ferromagnetism at the LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface PhD Thesis
2015.
Links | BibTeX | Tags: AMR, epitaxial, Kondo effect, Magnetic force microscopy, Magnetism, Mesoscopic quantum transport, scanning probe, Superconductivity, vortex dynamics
@phdthesis{Mehta2015,
title = {Interplay between superconductivity and ferromagnetism at the LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface},
author = {Manan Mehta},
url = {http://www.nano.northwestern.edu/wp-content/uploads/2017/09/Manan_Mehta_PhD_Thesis.pdf},
year = {2015},
date = {2015-12-01},
keywords = {AMR, epitaxial, Kondo effect, Magnetic force microscopy, Magnetism, Mesoscopic quantum transport, scanning probe, Superconductivity, vortex dynamics},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {phdthesis}
}
Scott Mayle; Tanuj Gupta; Sam Davis; Venkat Chandrasekhar; Serhii Shafraniuk
Thermometry and thermal management of carbon nanotube circuits Journal Article
In: Journal of Applied Physics, vol. 117, no. 19, pp. 194305, 2015, ISSN: 0021-8979, 1089-7550.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Nanotube, thermal transport
@article{mayle_thermometry_2015,
title = {Thermometry and thermal management of carbon nanotube circuits},
author = { Scott Mayle and Tanuj Gupta and Sam Davis and Venkat Chandrasekhar and Serhii Shafraniuk},
url = {http://scitation.aip.org/content/aip/journal/jap/117/19/10.1063/1.4918667},
doi = {10.1063/1.4918667},
issn = {0021-8979, 1089-7550},
year = {2015},
date = {2015-05-01},
urldate = {2015-10-23},
journal = {Journal of Applied Physics},
volume = {117},
number = {19},
pages = {194305},
abstract = {Monitoring of the intrinsic temperature and the thermal management is discussed for the carbon nanotube nano-circuits. The experimental results concerning fabricating and testing of a thermometer able to monitor the intrinsic temperature on nanoscale are reported. We also suggest a model which describes a bi-metal multilayer system able to filter the heat flow, based on separating the electron and phonon components one from another. The bi-metal multilayer structure minimizes the phonon component of the heat flow, while retaining the electronic part. The method allows one to improve the overall performance of the electronic nano-circuits due to minimizing the energy dissipation.},
keywords = {Nanotube, thermal transport},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
V. V. Bal; M. M. Mehta; S. Ryu; H. Lee; C. M. Folkman; C. B. Eom; V. Chandrasekhar
Gate-tunable superconducting weak link behavior in top-gated LaAlO3-SrTiO3 Journal Article
In: Applied Physics Letters, vol. 106, no. 21, pp. 212601, 2015.
Links | BibTeX | Tags: epitaxial, Magnetism, perovskite, Proximity effect, Superconductivity
@article{bal_gate-tunable_2015,
title = {Gate-tunable superconducting weak link behavior in top-gated LaAlO3-SrTiO3},
author = { V. V. Bal and M. M. Mehta and S. Ryu and H. Lee and C. M. Folkman and C. B. Eom and V. Chandrasekhar},
url = {http://scitation.aip.org/content/aip/journal/apl/106/21/10.1063/1.4921924},
year = {2015},
date = {2015-01-01},
urldate = {2016-12-28},
journal = {Applied Physics Letters},
volume = {106},
number = {21},
pages = {212601},
keywords = {epitaxial, Magnetism, perovskite, Proximity effect, Superconductivity},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
M. M. Mehta; D. A. Dikin; C. W. Bark; S. Ryu; C. M. Folkman; C. B. Eom; V. Chandrasekhar
Magnetic field tuned superconductor-to-insulator transition at the LaAlO 3 / SrTiO 3 interface Journal Article
In: Physical Review B, vol. 90, no. 10, 2014, ISSN: 1098-0121, 1550-235X.
Links | BibTeX | Tags: epitaxial, insulator, Magnetism, perovskite, superconductor
@article{mehta_magnetic_2014,
title = {Magnetic field tuned superconductor-to-insulator transition at the LaAlO 3 / SrTiO 3 interface},
author = { M. M. Mehta and D. A. Dikin and C. W. Bark and S. Ryu and C. M. Folkman and C. B. Eom and V. Chandrasekhar},
url = {http://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevB.90.100506},
doi = {10.1103/PhysRevB.90.100506},
issn = {1098-0121, 1550-235X},
year = {2014},
date = {2014-01-01},
urldate = {2015-10-23},
journal = {Physical Review B},
volume = {90},
number = {10},
keywords = {epitaxial, insulator, Magnetism, perovskite, superconductor},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
M. M. Mehta; Venkat Chandrasekhar
A hybrid analog-digital phase-locked loop for frequency mode non-contact scanning probe microscopy Journal Article
In: Review of Scientific Instruments, vol. 85, no. 1, pp. 013707, 2014.
Links | BibTeX | Tags: instrumentation, scanning probe
@article{mehta_hybrid_2014,
title = {A hybrid analog-digital phase-locked loop for frequency mode non-contact scanning probe microscopy},
author = { M. M. Mehta and Venkat Chandrasekhar},
url = {http://scitation.aip.org/content/aip/journal/rsi/85/1/10.1063/1.4862818},
year = {2014},
date = {2014-01-01},
urldate = {2015-10-23},
journal = {Review of Scientific Instruments},
volume = {85},
number = {1},
pages = {013707},
keywords = {instrumentation, scanning probe},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Taewan Noh; Sam Davis; Venkat Chandrasekhar
Nonlocal correlations in a proximity-coupled normal-metal Journal Article
In: Physical Review B, vol. 88, no. 2, 2013, ISSN: 1098-0121, 1550-235X.
Links | BibTeX | Tags: Andreev reflection, Proximity effect, Superconductivity
@article{noh_nonlocal_2013,
title = {Nonlocal correlations in a proximity-coupled normal-metal},
author = { Taewan Noh and Sam Davis and Venkat Chandrasekhar},
url = {http://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevB.88.024502},
doi = {10.1103/PhysRevB.88.024502},
issn = {1098-0121, 1550-235X},
year = {2013},
date = {2013-07-01},
urldate = {2016-12-28},
journal = {Physical Review B},
volume = {88},
number = {2},
keywords = {Andreev reflection, Proximity effect, Superconductivity},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Taewan Noh; Manuel Houzet; Julia S. Meyer; Venkat Chandrasekhar
Nonlocal spin correlations mediated by a superconductor Journal Article
In: Physical Review B, vol. 87, no. 22, 2013, ISSN: 1098-0121, 1550-235X.
Links | BibTeX | Tags: Andreev reflection, Proximity effect, spin transport, Superconductivity
@article{noh_nonlocal_2013-1,
title = {Nonlocal spin correlations mediated by a superconductor},
author = { Taewan Noh and Manuel Houzet and Julia S. Meyer and Venkat Chandrasekhar},
url = {http://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevB.87.220502},
doi = {10.1103/PhysRevB.87.220502},
issn = {1098-0121, 1550-235X},
year = {2013},
date = {2013-06-01},
urldate = {2015-10-26},
journal = {Physical Review B},
volume = {87},
number = {22},
keywords = {Andreev reflection, Proximity effect, spin transport, Superconductivity},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Venkat Chandrasekhar; M. M. Mehta
RTSPM: Real-time Linux control software for scanning probe microscopy Journal Article
In: Review of Scientific Instruments, vol. 84, no. 1, pp. 013705, 2013.
Links | BibTeX | Tags: instrumentation, scanning probe
@article{chandrasekhar_rtspm:_2013,
title = {RTSPM: Real-time Linux control software for scanning probe microscopy},
author = { Venkat Chandrasekhar and M. M. Mehta},
url = {http://scitation.aip.org/content/aip/journal/rsi/84/1/10.1063/1.4775717},
year = {2013},
date = {2013-01-01},
urldate = {2015-10-21},
journal = {Review of Scientific Instruments},
volume = {84},
number = {1},
pages = {013705},
keywords = {instrumentation, scanning probe},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Venkat Chandrasekhar; Manan Mehta
A real-time software simulator for scanning force microscopy Unpublished
2013.
Links | BibTeX | Tags: instrumentation, scanning probe
@unpublished{chandrasekhar_real-time_2013,
title = {A real-time software simulator for scanning force microscopy},
author = { Venkat Chandrasekhar and Manan Mehta},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/1307.7679},
year = {2013},
date = {2013-01-01},
urldate = {2016-12-28},
keywords = {instrumentation, scanning probe},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {unpublished}
}
M.M. Mehta; D.A. Dikin; C.W. Bark; S. Ryu; C.M. Folkman; C.B. Eom; V. Chandrasekhar
Evidence for charge–vortex duality at the LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface Journal Article
In: Nature Communications, vol. 3, pp. 955, 2012, ISSN: 2041-1723.
Links | BibTeX | Tags: epitaxial, insulator, Magnetism, perovskite, Superconductivity
@article{mehta_evidence_2012,
title = {Evidence for charge–vortex duality at the LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface},
author = { M.M. Mehta and D.A. Dikin and C.W. Bark and S. Ryu and C.M. Folkman and C.B. Eom and V. Chandrasekhar},
url = {http://www.nature.com/doifinder/10.1038/ncomms1959},
doi = {10.1038/ncomms1959},
issn = {2041-1723},
year = {2012},
date = {2012-07-01},
urldate = {2015-10-23},
journal = {Nature Communications},
volume = {3},
pages = {955},
keywords = {epitaxial, insulator, Magnetism, perovskite, Superconductivity},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
P Cadden-Zimansky; J Wei; V Chandrasekhar
Coherent nonlocal correlations in Andreev interferometers Journal Article
In: New Journal of Physics, vol. 14, no. 4, pp. 043004, 2012, ISSN: 1367-2630.
Links | BibTeX | Tags: Andreev reflection, Proximity effect, superconductor
@article{cadden-zimansky_coherent_2012,
title = {Coherent nonlocal correlations in Andreev interferometers},
author = { P Cadden-Zimansky and J Wei and V Chandrasekhar},
url = {http://stacks.iop.org/1367-2630/14/i=4/a=043004?key=crossref.f07cad531c95baf1d401aa858682bf05},
doi = {10.1088/1367-2630/14/4/043004},
issn = {1367-2630},
year = {2012},
date = {2012-01-01},
urldate = {2016-12-28},
journal = {New Journal of Physics},
volume = {14},
number = {4},
pages = {043004},
keywords = {Andreev reflection, Proximity effect, superconductor},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Jian Wei; P. Cadden-Zimansky; V. Chandrasekhar; P. Virtanen
Thermal fluctuations and flux-tunable barrier in proximity Josephson junctions Journal Article
In: Physical Review B, vol. 84, no. 22, 2011, ISSN: 1098-0121, 1550-235X.
Links | BibTeX | Tags: Andreev reflection, Proximity effect, Superconductivity
@article{wei_thermal_2011,
title = {Thermal fluctuations and flux-tunable barrier in proximity Josephson junctions},
author = { Jian Wei and P. Cadden-Zimansky and V. Chandrasekhar and P. Virtanen},
url = {http://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevB.84.224519},
doi = {10.1103/PhysRevB.84.224519},
issn = {1098-0121, 1550-235X},
year = {2011},
date = {2011-12-01},
urldate = {2016-12-29},
journal = {Physical Review B},
volume = {84},
number = {22},
keywords = {Andreev reflection, Proximity effect, Superconductivity},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
D. A. Dikin; M. Mehta; C. W. Bark; C. M. Folkman; C. B. Eom; V. Chandrasekhar
Coexistence of Superconductivity and Ferromagnetism in Two Dimensions Journal Article
In: Physical Review Letters, vol. 107, no. 5, 2011, ISSN: 0031-9007, 1079-7114.
Links | BibTeX | Tags: epitaxial, Magnetism, perovskite, Superconductivity
@article{dikin_coexistence_2011,
title = {Coexistence of Superconductivity and Ferromagnetism in Two Dimensions},
author = { D. A. Dikin and M. Mehta and C. W. Bark and C. M. Folkman and C. B. Eom and V. Chandrasekhar},
url = {http://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevLett.107.056802},
doi = {10.1103/PhysRevLett.107.056802},
issn = {0031-9007, 1079-7114},
year = {2011},
date = {2011-07-01},
urldate = {2015-10-26},
journal = {Physical Review Letters},
volume = {107},
number = {5},
keywords = {epitaxial, Magnetism, perovskite, Superconductivity},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Goutam Sheet; Manan Mehta; D. A. Dikin; S. Lee; C. W. Bark; J. Jiang; J. D. Weiss; E. E. Hellstrom; M. S. Rzchowski; C. B. Eom; V. Chandrasekhar
Phase-Incoherent Superconducting Pairs in the Normal State of Ba ( Fe 1 − x Co x ) 2 As 2 Journal Article
In: Physical Review Letters, vol. 105, no. 16, 2010, ISSN: 0031-9007, 1079-7114.
Links | BibTeX | Tags: Andreev reflection, Superconductivity
@article{sheet_phase-incoherent_2010,
title = {Phase-Incoherent Superconducting Pairs in the Normal State of Ba ( Fe 1 − x Co x ) 2 As 2},
author = { Goutam Sheet and Manan Mehta and D. A. Dikin and S. Lee and C. W. Bark and J. Jiang and J. D. Weiss and E. E. Hellstrom and M. S. Rzchowski and C. B. Eom and V. Chandrasekhar},
url = {http://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevLett.105.167003},
doi = {10.1103/PhysRevLett.105.167003},
issn = {0031-9007, 1079-7114},
year = {2010},
date = {2010-10-01},
urldate = {2016-12-28},
journal = {Physical Review Letters},
volume = {105},
number = {16},
keywords = {Andreev reflection, Superconductivity},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Manan Mehta; Goutam Sheet; D. A. Dikin; S. Lee; C. W. Bark; J. Jiang; J. D. Weiss; E. E. Hellstrom; M. S. Rzchowski; C. B. Eom; V. Chandrasekhar
Conductance asymmetry in point-contacts on epitaxial thin films of Ba(Fe0.92Co0.08)2As2 Journal Article
In: Applied Physics Letters, vol. 97, no. 1, pp. 012503, 2010, ISSN: 0003-6951, 1077-3118.
Links | BibTeX | Tags: Andreev reflection, epitaxial, perovskite, Superconductivity
@article{mehta_conductance_2010,
title = {Conductance asymmetry in point-contacts on epitaxial thin films of Ba(Fe0.92Co0.08)2As2},
author = { Manan Mehta and Goutam Sheet and D. A. Dikin and S. Lee and C. W. Bark and J. Jiang and J. D. Weiss and E. E. Hellstrom and M. S. Rzchowski and C. B. Eom and V. Chandrasekhar},
url = {http://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/1.3460274},
doi = {10.1063/1.3460274},
issn = {0003-6951, 1077-3118},
year = {2010},
date = {2010-07-01},
urldate = {2016-12-28},
journal = {Applied Physics Letters},
volume = {97},
number = {1},
pages = {012503},
keywords = {Andreev reflection, epitaxial, perovskite, Superconductivity},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Jian Wei; Venkat Chandrasekhar
Positive noise cross-correlation in hybrid superconducting and normal-metal three-terminal devices Journal Article
In: Nature Physics, vol. 6, pp. 494-498, 2010.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Andreev reflection, crossed andreev reflection, Proximity effect, Superconductivity
@article{Wei2010,
title = {Positive noise cross-correlation in hybrid superconducting and normal-metal three-terminal devices},
author = {Jian Wei and Venkat Chandrasekhar},
url = {https://www.nature.com/articles/nphys1669},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1669},
year = {2010},
date = {2010-05-16},
journal = {Nature Physics},
volume = {6},
pages = {494-498},
abstract = {Non-local entanglement is a key ingredient to quantum information processing. For photons, entanglement has been demonstrated, but it is more difficult to observe for electrons. One approach is to use a superconductor, where electrons form spin-entangled Cooper pairs, which is a natural source for entangled electrons. For a three-terminal device consisting of a superconductor sandwiched between two normal metals, it has been predicted that Cooper pairs can split into spin-entangled electrons flowing in the two spatially separated normal metals resulting in a negative non-local resistance and a positive current–current correlation. The former prosperity has been observed, but not the latter. Here we show that both characteristics can be observed, consistent with Cooper-pair splitting. Moreover, the splitting efficiency can be tuned by independently controlling the energy of the electrons passing the two superconductor/normal-metal interfaces, which may lead to better understanding and control of non-local entanglement.},
keywords = {Andreev reflection, crossed andreev reflection, Proximity effect, Superconductivity},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Goutam Sheet; Alexandra R. Cunliffe; Erik J. Offerman; Chad M. Folkman; Chang-Beom Eom; Venkat Chandrasekhar
dc and high frequency magnetic properties of nanopatterned CoFe2O4 arrays fabricated using sol-gel precursors Journal Article
In: Journal of Applied Physics, vol. 107, no. 10, pp. 104309, 2010, ISSN: 0021-8979, 1089-7550.
Links | BibTeX | Tags: Magnetism, microwave, perovskite, scanning probe
@article{sheet_dc_2010,
title = {dc and high frequency magnetic properties of nanopatterned CoFe2O4 arrays fabricated using sol-gel precursors},
author = { Goutam Sheet and Alexandra R. Cunliffe and Erik J. Offerman and Chad M. Folkman and Chang-Beom Eom and Venkat Chandrasekhar},
url = {http://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/1.3393745},
doi = {10.1063/1.3393745},
issn = {0021-8979, 1089-7550},
year = {2010},
date = {2010-05-01},
urldate = {2016-12-28},
journal = {Journal of Applied Physics},
volume = {107},
number = {10},
pages = {104309},
keywords = {Magnetism, microwave, perovskite, scanning probe},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Goutam Sheet; Venkat Chandrasekhar
Possible microscopic origin of large broadening parameter in point Andreev reflection spectroscopy Journal Article
In: Applied Physics Letters, vol. 97, no. 6, pp. 062507, 2010, ISSN: 0003-6951, 1077-3118.
Links | BibTeX | Tags: Andreev reflection, perovskite, point contact, Superconductivity
@article{sheet_possible_2010,
title = {Possible microscopic origin of large broadening parameter in point Andreev reflection spectroscopy},
author = { Goutam Sheet and Venkat Chandrasekhar},
url = {http://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/1.3479927},
doi = {10.1063/1.3479927},
issn = {0003-6951, 1077-3118},
year = {2010},
date = {2010-01-01},
urldate = {2016-12-29},
journal = {Applied Physics Letters},
volume = {97},
number = {6},
pages = {062507},
keywords = {Andreev reflection, perovskite, point contact, Superconductivity},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Venkat Chandrasekhar
Thermal transport in superconductor/normal-metal structures Journal Article
In: Supercond. Sci. Technol., vol. 22, no. 8, pp. 083001, 2009, ISSN: 0953-2048.
Links | BibTeX | Tags: Proximity effect, Superconductivity, thermal transport
@article{chandrasekhar_thermal_2009,
title = {Thermal transport in superconductor/normal-metal structures},
author = { Venkat Chandrasekhar},
url = {http://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/0953-2048/22/8/083001/meta},
doi = {10.1088/0953-2048/22/8/083001},
issn = {0953-2048},
year = {2009},
date = {2009-07-01},
urldate = {2016-12-28},
journal = {Supercond. Sci. Technol.},
volume = {22},
number = {8},
pages = {083001},
keywords = {Proximity effect, Superconductivity, thermal transport},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Alexandra R. Cunliffe
2009.
Links | BibTeX | Tags: AMR, epitaxial, FMR, Magnetic force microscopy, Magnetism, nanomagnets, perovskite, scanning probe
@mastersthesis{Cunliffe2009,
title = {Magnetoelectric cobalt ferrite/bismuth ferrite hybrid nanostructures: Progress towards achieving electric field control of magnetization},
author = {Alexandra R. Cunliffe},
url = {http://www.nano.northwestern.edu/wp-content/uploads/2017/09/Senior_Thesis.pdf},
year = {2009},
date = {2009-05-01},
keywords = {AMR, epitaxial, FMR, Magnetic force microscopy, Magnetism, nanomagnets, perovskite, scanning probe},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {mastersthesis}
}
Paul Cadden-Zimansky; Jian Wei; Venkat Chandrasekhar
Cooper-pair-mediated coherence between two normal metals Journal Article
In: Nature Physics, vol. 5, pp. 393–397, 2009.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Andreev reflection, crossed andreev reflection, Proximity effect, Superconductivity
@article{Cadden-Zimansky2009,
title = {Cooper-pair-mediated coherence between two normal metals},
author = {Paul Cadden-Zimansky and Jian Wei and Venkat Chandrasekhar},
url = {https://www.nature.com/articles/nphys1252?foxtrotcallback=true},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1252},
year = {2009},
date = {2009-04-26},
journal = {Nature Physics},
volume = {5},
pages = {393–397},
abstract = {Two electrons bound in a singlet state have long provided a conceptual and pedagogical framework for understanding the non-local nature of entangled quantum objects. As bound singlet electrons separated by a coherence length of up to several hundred nanometres occur naturally in conventional Bardeen–Cooper–Schrieffer superconductors in the form of Cooper pairs, recent theoretical investigations have focused on whether electrons in spatially separated normal-metal probes placed within a coherence length of each other on a superconductor can be quantum mechanically coupled by the singlet pairs. This coupling is predicted to occur through the non-local processes of elastic cotunnelling and crossed Andreev reflection. In crossed Andreev reflection, the constituent electrons of a Cooper pair are sent into different normal probes while retaining their mutual coherence. In elastic cotunnelling, a sub-gap electron approaching the superconductor from one normal probe undergoes coherent, long-range tunnelling to the second probe that is mediated by the Cooper pairs in the condensate. Here, we present experimental evidence for coherent, non-local coupling between electrons in two normal metals linked by a superconductor. The coupling is observed in non-local resistance oscillations that are periodic in an externally applied magnetic flux.},
keywords = {Andreev reflection, crossed andreev reflection, Proximity effect, Superconductivity},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Irma Kuljanishvili; Dmitriy A. Dikin; Sergey Rozhok; Scott Mayle; Venkat Chandrasekhar
Controllable Patterning and CVD Growth of Isolated Carbon Nanotubes with Direct Parallel Writing of Catalyst Using Dip-Pen Nanolithography Journal Article
In: Small, vol. 5, no. 22, pp. 2523–2527, 2009, ISSN: 16136810, 16136829.
Links | BibTeX | Tags: Nanotube, scanning probe
@article{kuljanishvili_controllable_2009,
title = {Controllable Patterning and CVD Growth of Isolated Carbon Nanotubes with Direct Parallel Writing of Catalyst Using Dip-Pen Nanolithography},
author = { Irma Kuljanishvili and Dmitriy A. Dikin and Sergey Rozhok and Scott Mayle and Venkat Chandrasekhar},
url = {http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/smll.200900841},
doi = {10.1002/smll.200900841},
issn = {16136810, 16136829},
year = {2009},
date = {2009-01-01},
urldate = {2015-10-23},
journal = {Small},
volume = {5},
number = {22},
pages = {2523--2527},
keywords = {Nanotube, scanning probe},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Paul Cadden-Zimansky
Nonlocal Coherence in Normal Metal-Superconductor Nanostructures PhD Thesis
2008.
Links | BibTeX | Tags: Andreev reflection, charge imbalance, crossed andreev reflection, Mesoscopic quantum transport, nanomagnets, phase coherence, Proximity effect, Superconductivity
@phdthesis{Cadden-Zimansky2008,
title = {Nonlocal Coherence in Normal Metal-Superconductor Nanostructures},
author = {Paul Cadden-Zimansky},
url = {http://www.nano.northwestern.edu/wp-content/uploads/2017/09/C-Z-Thesis-Final.pdf},
year = {2008},
date = {2008-12-01},
keywords = {Andreev reflection, charge imbalance, crossed andreev reflection, Mesoscopic quantum transport, nanomagnets, phase coherence, Proximity effect, Superconductivity},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {phdthesis}
}
Udai Raj Singh; Anjan K. Gupta; Goutam Sheet; Venkat Chandrasekhar; H. W. Jang; C. B. Eom
Pseudogap formation in the metallic state of La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 thin films Journal Article
In: Applied Physics Letters, vol. 93, no. 21, pp. 212503, 2008, ISSN: 0003-6951, 1077-3118.
Links | BibTeX | Tags: Andreev reflection, point contact, scanning probe, Superconductivity
@article{singh_pseudogap_2008,
title = {Pseudogap formation in the metallic state of La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 thin films},
author = { Udai Raj Singh and Anjan K. Gupta and Goutam Sheet and Venkat Chandrasekhar and H. W. Jang and C. B. Eom},
url = {http://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/1.3028072},
doi = {10.1063/1.3028072},
issn = {0003-6951, 1077-3118},
year = {2008},
date = {2008-11-01},
urldate = {2016-12-28},
journal = {Applied Physics Letters},
volume = {93},
number = {21},
pages = {212503},
keywords = {Andreev reflection, point contact, scanning probe, Superconductivity},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}